Spring
By reducing boiler-plate code and providing easy development of Web along with data, Spring Framework was developed based on Java EE.
The Spring Framework (Spring) is an open-source application framework that provides infrastructure support for developing Java applications. One of the most popular Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) frameworks, Spring helps developers create high performing applications using plain old Java objects (POJOs).
A framework is a large body of predefined code to which developers can add code to solve a problem in a specific domain. There are many popular Java frameworks including Java Server Faces (JSF), Maven, Hibernate, Struts, and Spring.
Spring Boot was later developed based on Spring Framework which enabled creating Spring-based applications as simple as running a single command thereby nullifying the gap between the manual configurations while setting up the Spring Framework. This allowed development and deployment of Spring based applications faster and easier.
Later, Spring Cloud was built on top of Spring Boot and simplified the development of applications with distributed architectures(microservices architectures) which often had many common patterns like service discovery and distributed configuration. Spring Cloud helped developers to make it easier to build applications based on those patterns.
Why Spring?
Spring came as an alternative to Java EE. Now, Spring is much more a complimentary to JEE. Spring is flexible, modular and backward compatible and also enabled us to pick and choose whichever parts of spring makes the most sense for our project. Spring has large and active community. Spring is an open-source project which continually innovates and evolves and backed by Pivotal company.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot is a microservice-based framework and making a production-ready application in it takes very less time.
Layers in Spring Boot:
There are four main layers in Spring Boot:
- Presentation Layer: As the name suggests, it consists of views(i.e. frontend part)
- Data Access Layer: CRUD (create, retrieve, update, delete) operations on the database comes under this category.
- Service Layer: This consist of service classes and uses services provided by data access layers.
- Integration Layer: It consists of web different web services(any service available over the internet and uses XML messaging system).
Notable Features:
1. Intelligent Auto-configurations:
a. Attempts to automatically configure the spring application based on the
dependencies that were added.
b. Setting up auto-configuration is effortless
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class DemoApplication{
…
}
2. Can be run as a Standalone application.
a. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-ready Spring-based applications that we can 'just run'.
3. Opinionated (Spring Boot behaves on its own way)>
a. SpringBoot favors convention over configuration and is designed to get you up and running as fast as possible.
Spring Initializer helps us create the template for our application in an easy way by helping us adding Project Metadata and adding Dependencies
Key areas of Spring Framework:
- Core
- Web
- Aspect Oriented Programming
- Data Access
- Integration
- Testing
Spring Core:
- Spring Core is the foundational module upon which every other module is built.
- It provides,
- i18n Internationalization Support
- Validation Support
- Data Binding Support
- Type Conversion Support
- and more..
- Dependency Injection:
- Dependency Injection is about dealing with the way how objects depend on other objects and also about fulfilling the dependencies between one or more objects.
- Fulfilling dependencies:
- The object fulfills its own dependencies
- The object declares what it depends on and we manage how the dependency is fulfilled. ( THIS IS DEPENDENCY INJECTION )
- Fulfilling dependencies:
- Dependency Injection is about dealing with the way how objects depend on other objects and also about fulfilling the dependencies between one or more objects.
Spring Web:
- Framework for handling web requests
- Spring MVC
- Spring WebFlux
Spring Web MVC:
Model -> View -> Controller
Servlet API:
(Java) Servlet: A servlet is an object that receives a request and generates a response based on that request.
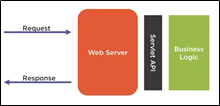 A standard request using the Servlet API
A standard request using the Servlet API
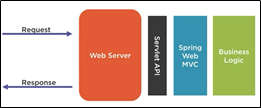 A standard request using Spring Web MVC Framework
A standard request using Spring Web MVC Framework
Thus, Spring MVC provides a 'Higher Level API' for the developer to interact with where the code development has made easier.
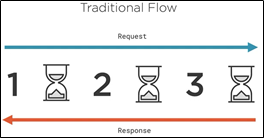
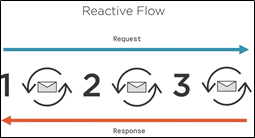
Spring WebFlux:
- A different way of handling web requests
- React rather than wait
- Asynchronous execution of web requests
- Doesn't block or wait for another request
Spring Aspect-Oriented Programming:
Aspect-oriented programming is a programming paradigm that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting concerns. So, AOP is a way of programming that increases organization of code for concerns that spans multiple tiers of an application.
Benefits of Spring AOP:
- Used to implement certain features in Spring
- A valuable tool for developers to handle cross-cutting concerns.
- Security is one of the example of something that AOP can solve.
public void sensitiveOperation(){
//check if the user has been authenticated and has specific role
if(...){
//do sensitive operation
}else{
// raise error and log operation and redirect to main page.
}
Example of an Application Security
#@PreAuthorize(hasRole())
public void sensitiveOperation(){
//do sensitive operation
}
Example of an Application Security using Spring AOP
Spring Data Access:
- Spring Data Access removes the purpose of boiler-plate code and enables us to work with APIs to access data.
- Spring Data Access provides super easy database transactions.
- Transactions is a general unit of work which must happen all together or not at all.
- Exception Translation : Data Access Module takes the SQL Error Codes and makes exceptions with a single method like "DataIntegrityViolationException".
- Testing data is easier with Spring Data Access Module.
- Easy to switch configurations for testing.
Spring Integration:
- How one application talks to one another?
- Spring Integration helps communicating with many services using templates like 'RESTTemplate'.
- Abstracts away tedious details.
- Sending the command.
- Handling the response.
- Spring Integration helps communicating with many services using templates like 'RESTTemplate'.
Spring Testing:
- Different ways to test
- Unit Testing
- Smallest testable parts are individually/independently tested.
- Dependencies causes challenges
- But, Spring's dependency injection forces developers to declare dependencies and control how the dependencies behave.
- Only tests the code, not the dependency.
- Mocks dependencies.
- Explicit support for unit testing is minimal.
- Smallest testable parts are individually/independently tested.
- Integration Testing
- Individual modules are combined and tested as a group, occurs after unit testing.
- Spring Framework plays an important role by piecing together various parts of an application for testing
- Spring provides support for common testing scenarios
- Setting up & testing data access
- Web application testing to ensure they are functional
- Ability to clean up stuffs after test.
- Unit Testing
- Spring Framework comes with several built-in mocks to make testing easier and faster.
Advantages of using Spring:
- Rock-solid & well engineered
- Wealth of existing knowledge to learn Spring
- Scalable
Disadvantages of Spring:
- Steep learning curve
- Size of the product increases
- Hard to debug
- Adds more memory overhead
- Complexity has grown over time
That's it for today. Meet you all in the next article.
Until then, See ya !
வாழ்க தமிழ் ! வளர்க தமிழினம் ! 🟥🟨
